Industry Insights
Home > News > Industry Insight > Application of WecLac® Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum BL21 and Ligilactobacillus salivarius LS97 Composition in Alleviating Gouty Arthritis
Application of WecLac® Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum BL21 and Ligilactobacillus salivarius LS97 Composition in Alleviating Gouty Arthritis
Abstract
This journal explores a novel probiotic composition designed to alleviate gouty arthritis. The composition consists of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum BL21 and Ligilactobacillus salivarius LS97. The synergistic effect of these strains demonstrates significant potential in reducing inflammation, pain, and other symptoms associated with gouty arthritis.
Introduction
Gout is a severe condition affecting joint health, closely related to disorders in uric acid metabolism. Elevated uric acid levels lead to the formation of uric acid crystals in joints, causing intense pain and inflammation. Traditional treatments focus on managing symptoms and preventing acute attacks. However, the role of gut microbiota in uric acid metabolism suggests that probiotics could be a promising therapeutic strategy.
Background
Probiotics are known to promote gut health by balancing beneficial bacteria. This balance can influence uric acid metabolism, potentially reducing uric acid levels and alleviating gout symptoms. This invention leverages the complementary effects of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum BL21 and Ligilactobacillus salivarius LS97 to enhance therapeutic outcomes for gouty arthritis patients.
Methods and Materials
Probiotic Strains
1. Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum BL21 (CGMCC No. 10452)
Collected from the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on January 27, 2015.
2. Ligilactobacillus salivarius LS97 (CGMCC No. 16922)
Collected from the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on December 10, 2018.
Preparation of Probiotic Composition
1. Cultivation: Both strains were separately cultivated in suitable media.
2. Fermentation: The fermentation process involved activation and fermentation to produce a substantial quantity of the probiotic cultures.
3. Harvesting: The cultures were centrifuged, and the supernatant was mixed with lyophilization protectants.
4. Lyophilization: The mixture was lyophilized to obtain probiotic powders.
5. Mixing: The probiotic powders were mixed in specific ratios (1:10 to 10:1) to form the final composition.
Results
In Vitro Studies
The probiotic combination exhibited the following effects:
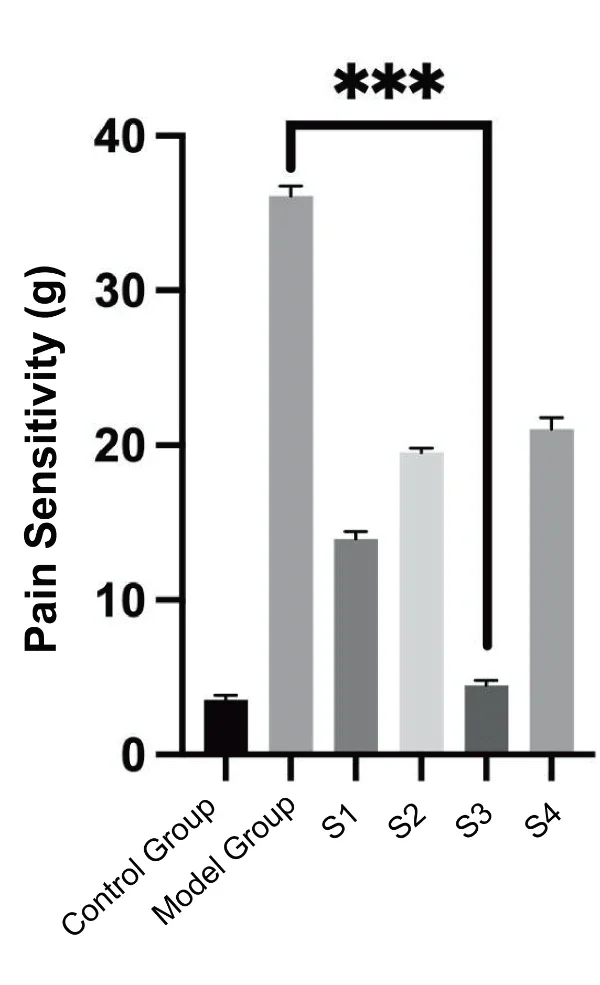
1. Pain Sensitivity: Significant reduction in pain sensitivity.
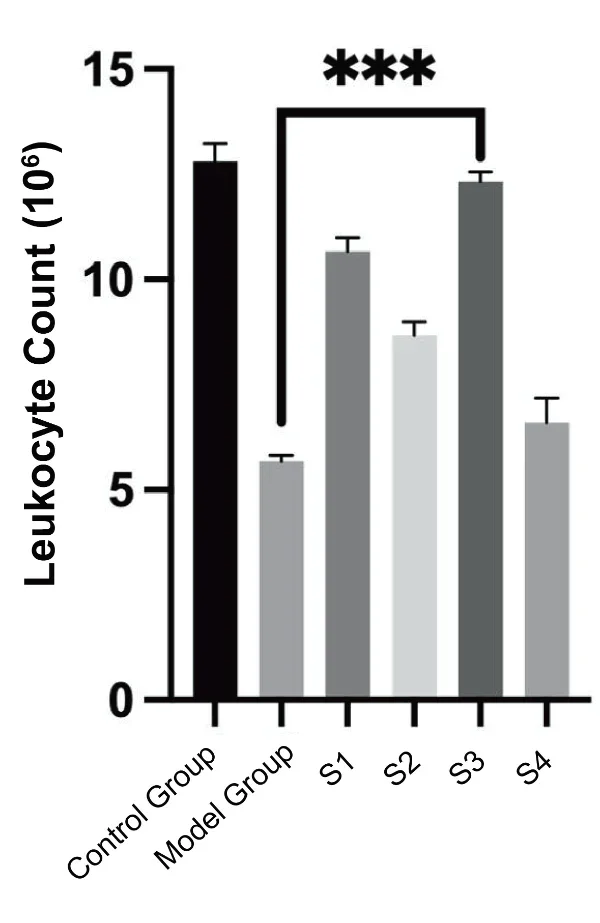
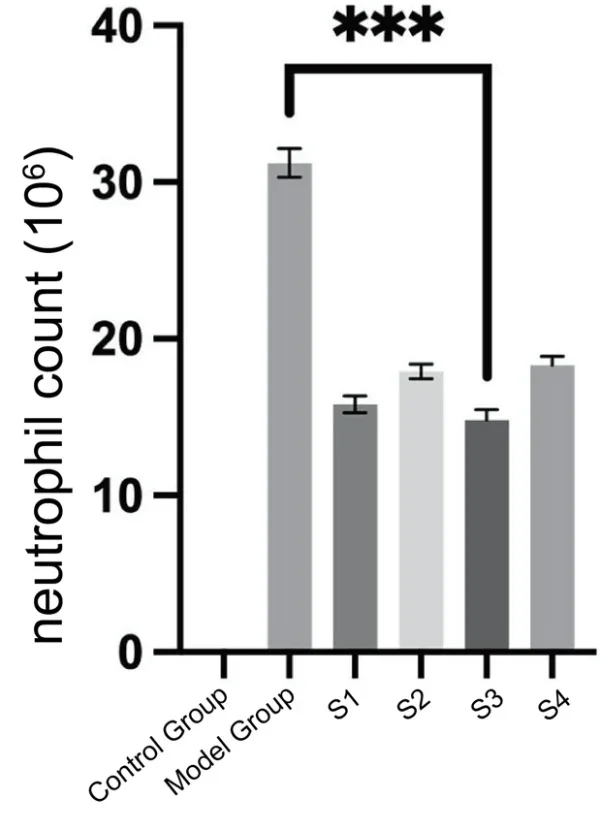
2. Leukocyte Count: Decrease in leukocyte and neutrophil aggregation in joint fluid.
3. Myeloperoxidase Activity: Lower myeloperoxidase activity in surrounding tissues.
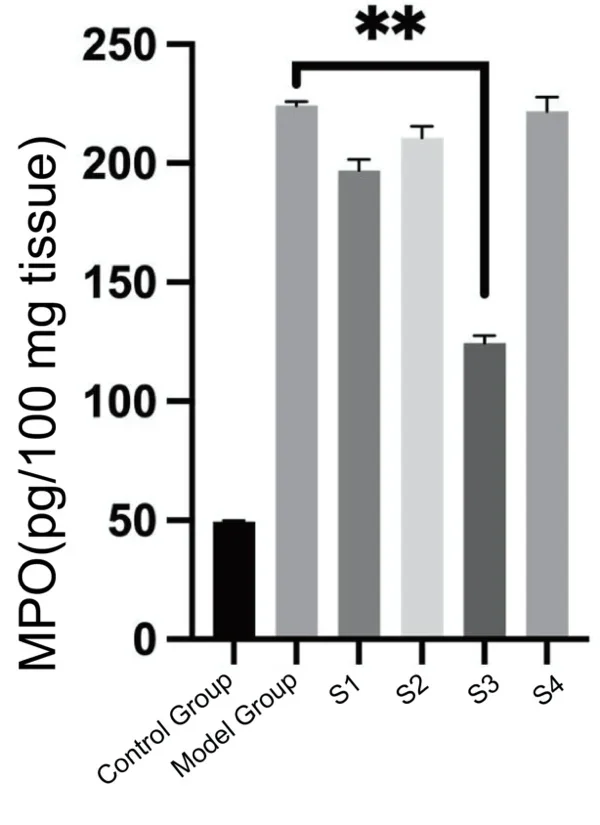
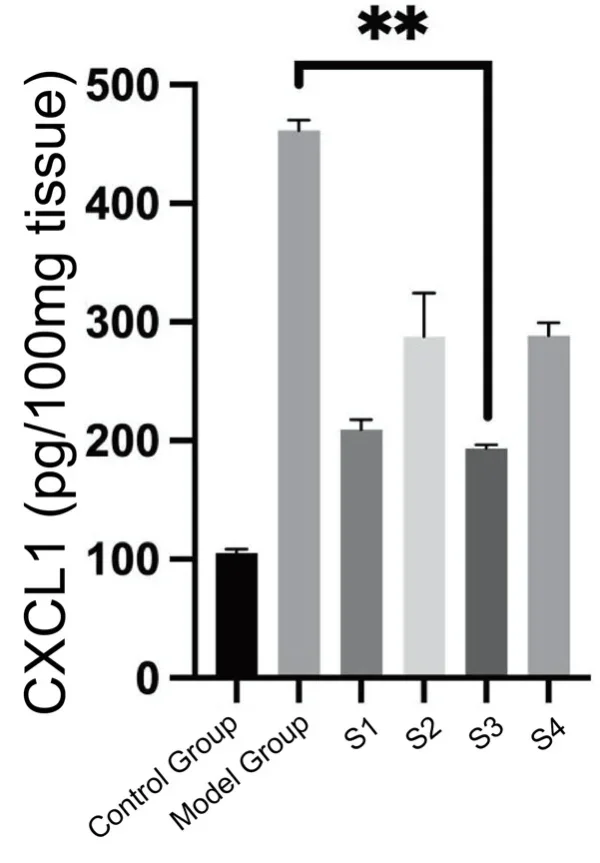
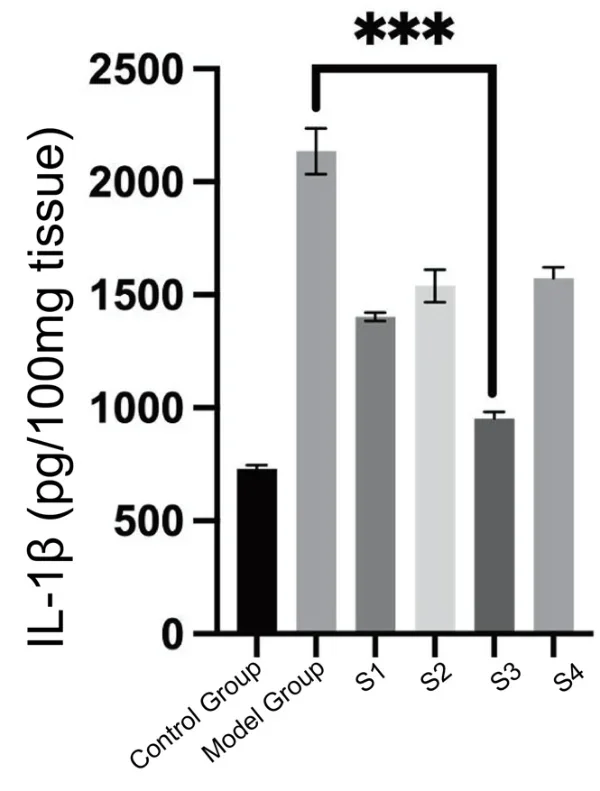
4. Inflammatory Cytokines: Reduced production of inflammatory cytokines CXCL1 and IL-1β.
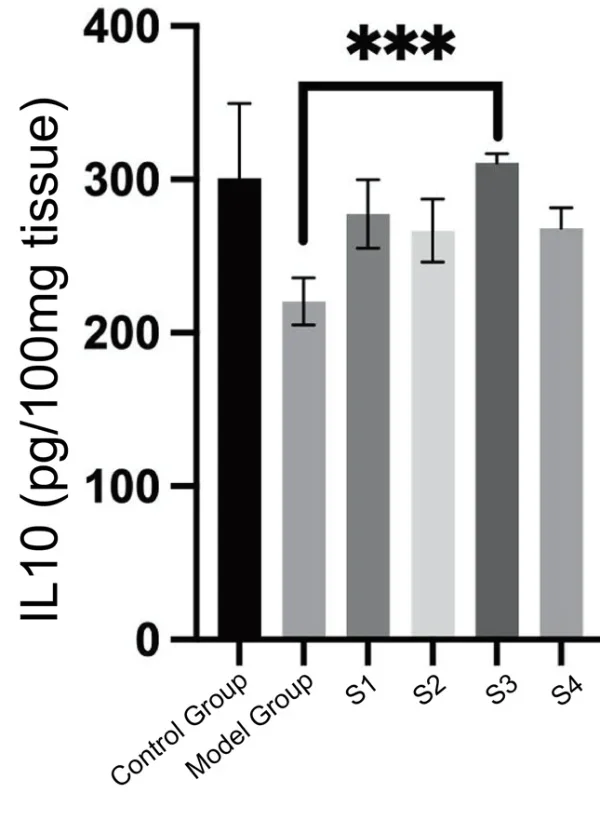
5. Anti-inflammatory Cytokines: Increased levels of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10.
Discussion
The synergistic interaction between Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum BL21 and Ligilactobacillus salivarius LS97 enhances their anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties. This combination can be utilized in various formulations, including lyophilized powders, capsules, tablets, and granules, to offer a safe and effective treatment for gouty arthritis.
Conclusion
This innovative probiotic composition presents a promising alternative for the prevention and treatment of gouty arthritis. The combination of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum BL21 and Ligilactobacillus salivarius LS97 not only alleviates symptoms but also addresses the underlying inflammatory processes. Further clinical studies are warranted to validate these findings and optimize dosage forms for maximum therapeutic benefit.






 Leave a Message
Leave a Message Email
Email Linkedin
Linkedin