Industry Insights
Home > News > Industry Insight > A Novel Breakthrough in Parkinson’s Disease Therapy: Mechanisms Underlying Probiotic Akk11-Mediated Concurrent Alleviation of Constipation and Depression
A Novel Breakthrough in Parkinson’s Disease Therapy: Mechanisms Underlying Probiotic Akk11-Mediated Concurrent Alleviation of Constipation and Depression

Parkinson’s disease (PD). Two recent high-impact studies from Wecare Research Institute show that this strain not only mitigates PD-related constipation but also ameliorates depressive phenotypes—two frequently comorbid, clinically intractable non-motor symptoms (NMS).
Researchers identified the gut as the shared pathological origin of these comorbid symptoms. Akk11 alleviates both by enhancing gut intrinsic regenerative capacity, opening a new avenue for microbe-based PD therapy.
1. Constipation and Depression: Earlier Onset and Greater Debilitating Effects
Beyond motor symptoms such as rest tremor and bradykinesia, PD patients often suffer from constipation and depression. These comorbid NMS synergistically impair quality of life. Due to unclear mechanisms, clinical management has long been symptomatic, lacking targeted treatment for their shared origin.
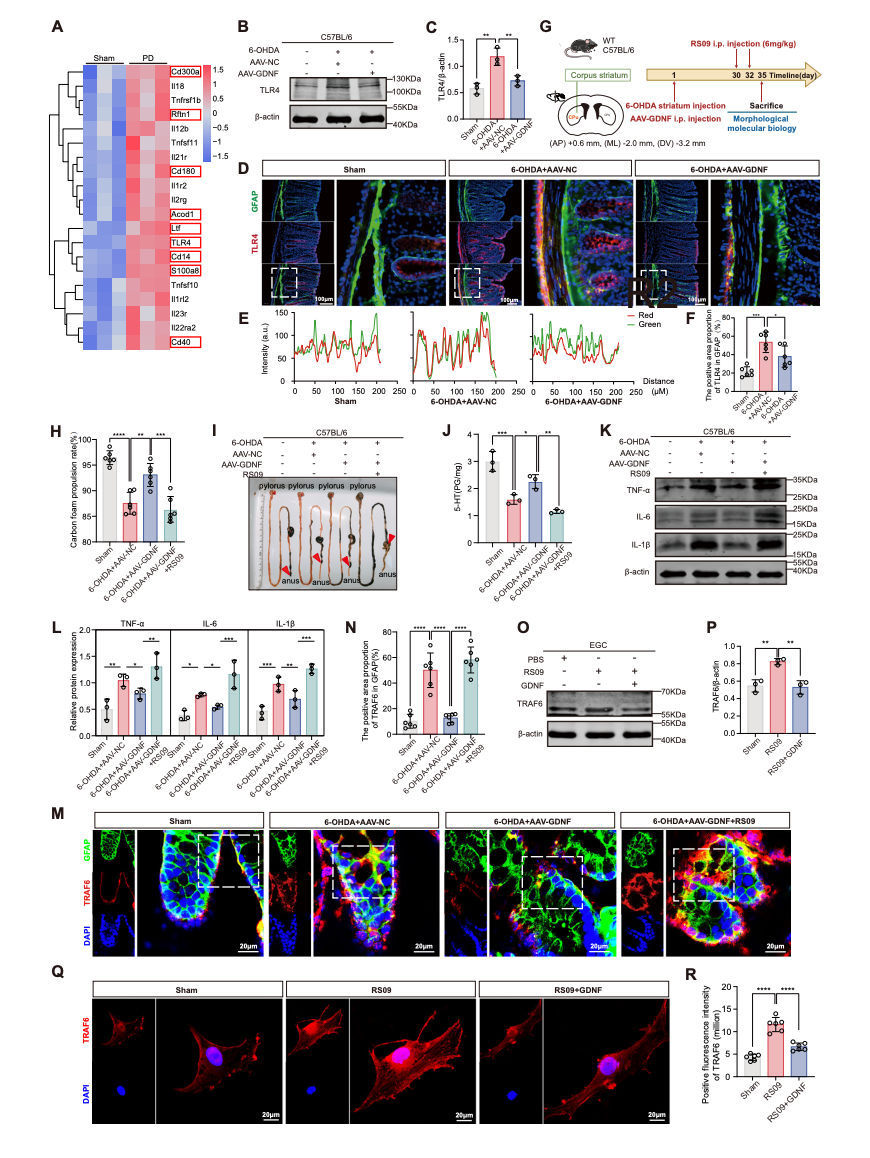
2. The Core Mechanism of "Gut-Brain Comorbidity"
The research team explored the gut-brain axis (GBA) to uncover the common pathological mechanisms underlying this comorbidity.
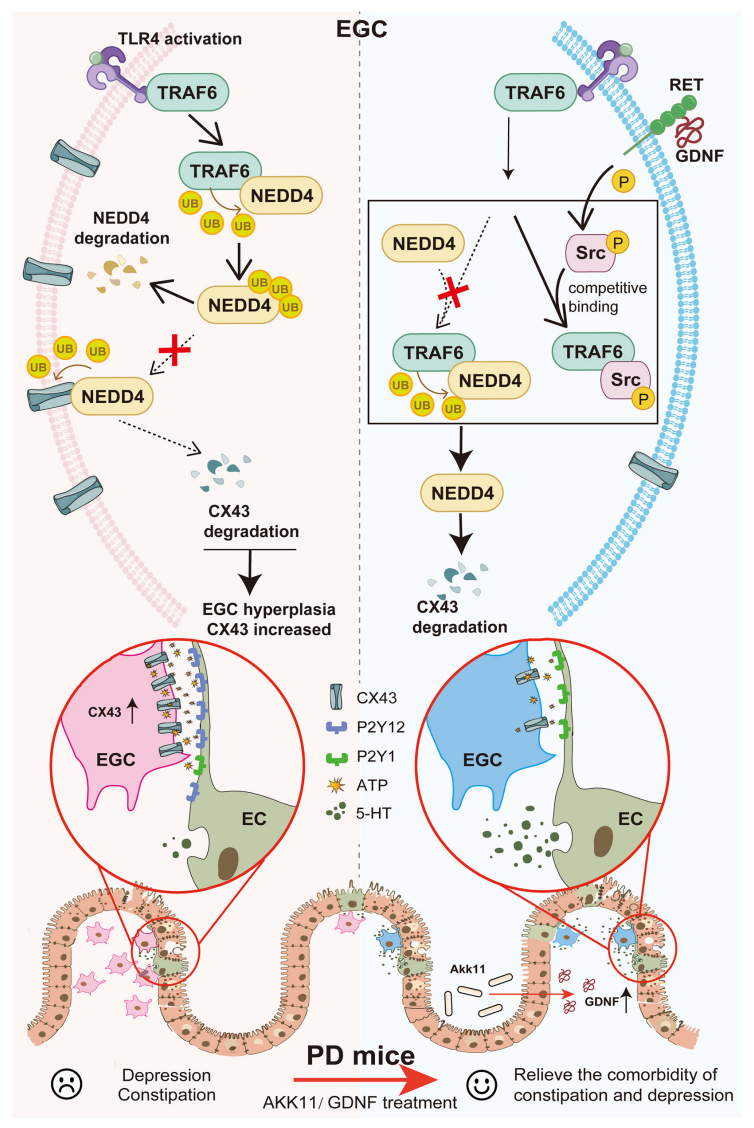
Studies revealed that in PD, colonic glial cells exhibit aberrant inflammatory activation via toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), inducing degradation of the key regulatory protein NEDD4 and triggering a pathological cascade:
l Accumulated extracellular ATP inhibits intestinal enterochromaffin cells, the primary producers of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT);
l Impaired 5-HT synthesis reduces intestinal motility (constipation) and diminishes central "pleasurable signaling" (depression).
This cascade, from intestinal inflammation to cerebral dysfunction, clarifies the shared etiology of these two debilitating PD symptoms for the first time.
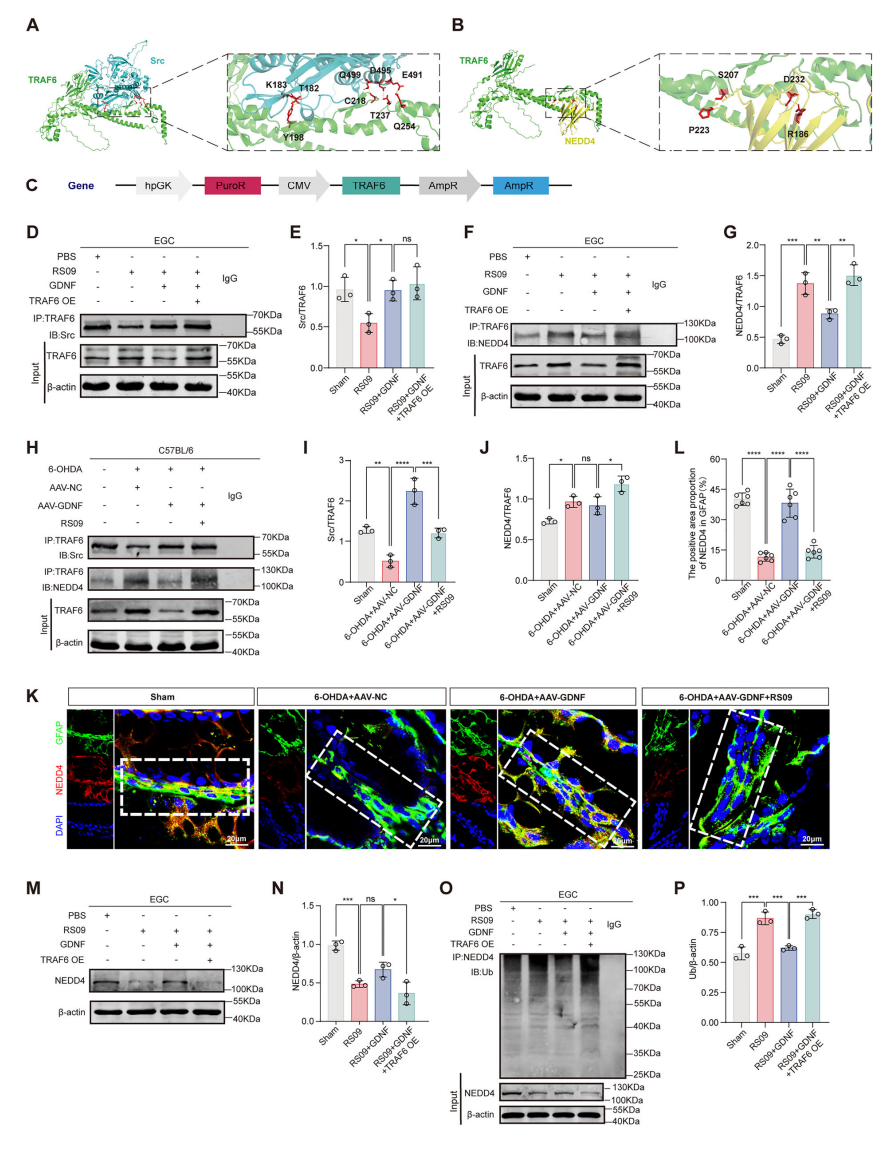
3. Probiotic Akk11 as a Key Catalyst for Gut-Brain Axis Repair
Two effective intervention strategies were identified for this pathological cascade:
1. Endogenous GDNF: Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (GDNF) stabilizes NEDD4, repairs CX43 hemichannels, and restores 5-HT synthesis, concurrently improving constipation and depression in PD animal models. However, its clinical application is limited by invasive delivery and high costs.
2. Probiotic Akk11: A more groundbreaking finding is that Akkermansia muciniphila strain Akk11 exhibits remarkable therapeutic potential. Akk11 stimulates endogenous GDNF synthesis in the gut, achieving therapeutic effects comparable to direct GDNF supplementation and alleviating both symptoms.
4. Ushering in a New Era of "Microbe-Gut-Brain Axis" Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease
This research’s significance extends beyond mechanism elucidation, providing revolutionary insights for PD therapeutics:
• For patients, oral administration of Akk11 offers a safe, convenient adjutant therapy to improve quality of life with minimal side effects, addressing unmet clinical needs.
• For the medical community, it validates gut microbiota modulation as a viable approach for neurological disorders, supporting microbiome-GBA research and novel therapeutic development.
In conclusion, this research shifts PD therapy from direct lesion antagonism to gut microenvironment restoration and endogenous regeneration activation. With the advancement of further preclinical and clinical studies, "microbe-mediated cerebral therapy" may soon transition to clinical practice, bringing new hope to millions of PD patients worldwide.
Reference
Mu, C. et al. GDNF signaling modulation by Akkermansia muciniphila ameliorates constipation–depression comorbidity in Parkinson's disease. npj Parkinsons Dis. 11, 342 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41531-025-01190-x
Wang, W. et al. Akkermansia muciniphila Akk11 Supplementation Attenuates MPTP-Induced Neurodegeneration by Inhibiting Microglial NLRP3 Inflammasome. Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. 17, 2348-2361 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-025-10499-1
Wang, X., Y. Fan, Y. Dong, et al. 2025. “ Strain-Specific Safety Evaluation of Akkermansia muciniphila Akk11: Comprehensive Genotypic, Phenotypic, and Toxicological Assessment.” Food Science & Nutrition 13, no. 11: e71154. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.71154.








 Leave a Message
Leave a Message Email
Email Linkedin
Linkedin